During a penetration test against the infrastructure of one of our clients we discovered a reflected Cross Site Scripting/HTML injection vulnerability in Microsoft Internet Information Services web server. The vulnerability could be exploited, with the help of user interaction, to inject javascript or html code in the browser of the victim in the context of a website hosted on IIS.
#### Versions Affected
* MS Internet Information services as deployed in the following Windows versions:
* Windows Vista
* Windows 7
* Windows 8.1 and RT 8.1
* Windows 2008 and 2008 r2
* Windows 2012 and 2012 r2
* Windows 2016
#### CVE Reference
CVE-2017-0055
Vendor Fix
Microsoft released bulletin MS017-16 and associated patches for each affected version
#### Vulnerability Type
XSS Elevation of Privilege
#### Severity Rating
Important
#### Description
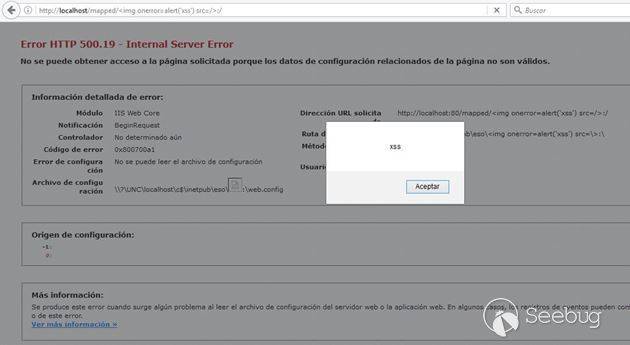
The default HTTP 500.19 error page of Internet Information Services fails to properly sanitize user-supplied input as rendered in the path where the Web.config file of the application or directory was attempted to be loaded.
Under normal conditions, any attempt to craft and visit an URL including javascript or html content on it will trigger either an HTTP 400 response from the server or will be handled by the customErrors Web.config setting of the application. We discovered that, if a website root hosted on IIS or any subfolder on it is located in a UNC path (NAS, shared folder or mapped drive), it is possible to craft a special link that, upon clicked, will trigger an HTTP 500.19 error page from the server rendering the javascript or html code injected as part of the path where the Web.config file was attempted to be loaded.
As the flaw lies in the fact of the improper sanitization of the 500.19 error page, other attack vectors not requiring UNC paths might exist.
#### Impact
By inducing a victim to click on a specially crafted link, is possible to execute javascript code in the victim’s browser in the context of a website hosted on IIS to conduct a classical reflected Cross Site Scripting (XSS) attack. The impact could be stealing user cookies, hijacking user session or performing unauthorized actions in the web application on behalf of the victim.
If the code injected is HTML, the vulnerability allows to conduct phishing attacks using the legitimate website against web application users.
#### Proof of concept
```http://vulnerableiis/uncpath/%3Cimg%20onerror=alert('xss')%20src=/%3E:/```
#### Mitigations
Neither ValidateRequest nor configuring customErrors setting on Web.config will protect from this, as this happens earlier in the request processing pipeline.


全部评论 (1)